1st Year Summer Exam Revision
Short Question TopicsPerspective
Equal widths Bisecting angles & lines Drawing hexagons & pentagons Isometric Graphs |
Long Question TopicsEllipse
Orthographic Transformations Isometric |
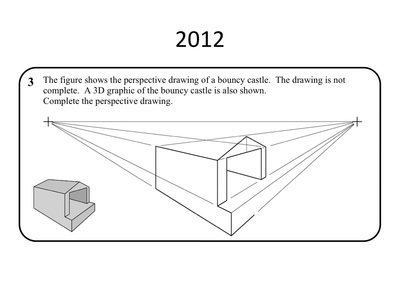
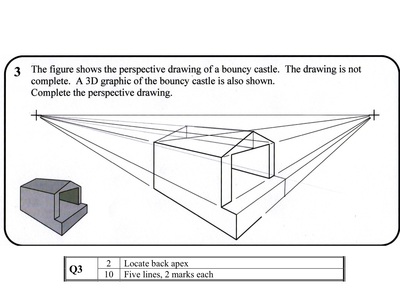
Perspective
Key Concepts:
- Vertical lines remain vertical
- Horizontal lines go to a vanishing point
- Find beginning and end of sloping lines, then join the dots
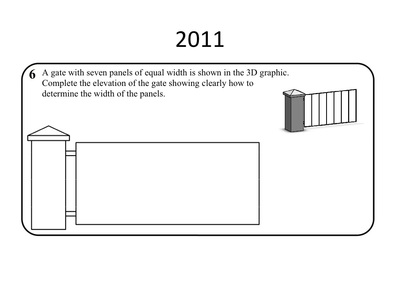
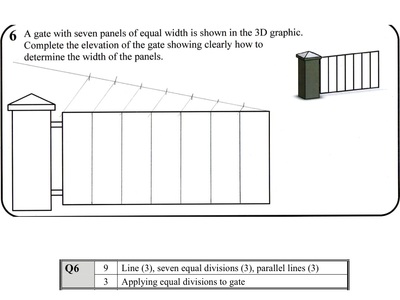
Equal Widths
Key Concepts:
If you have a line of unknown or awkward length (125.32mm),
There are two ways to divide up the line (step 2):
Very Important - You MUST you the construction method above, measuring the length and dividing it isn't accurate and will get you 0 marks.
Click here for revision questions (note: these will have to be printed)
If you have a line of unknown or awkward length (125.32mm),
- draw another line that you can easily divide into the amount of sections you need at an angle to the original line
- divide it up
- connect the end of the last division to the end of the original line
- draw lines parallel to the line in step 3 from each point
- the points where these lines meet the original line give you your divisions
There are two ways to divide up the line (step 2):
- use your compass to mark off equal divisions
- make the line a length that is easily divisible, ie, for 7 divisions use a 140mm line
Very Important - You MUST you the construction method above, measuring the length and dividing it isn't accurate and will get you 0 marks.
Click here for revision questions (note: these will have to be printed)
Bisecting Angles and Lines
This is a technique used within a range of short and long questions. See page XXX in your book for details of how to do this.
Drawing Hexagons and Pentagons
There are several ways to draw each of these so don't worry if you forget a part of a technique, there's always another option. Usually, using your compass is faster and easier than other methods.
Key angles
Pentagon (5 sides) - 72 degrees (360 / 5)
Hexagon (6 sides - 60 degrees (360 / 6)
Key angles
Pentagon (5 sides) - 72 degrees (360 / 5)
Hexagon (6 sides - 60 degrees (360 / 6)
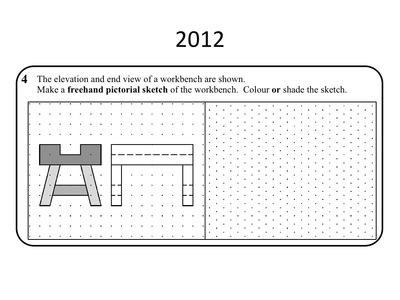
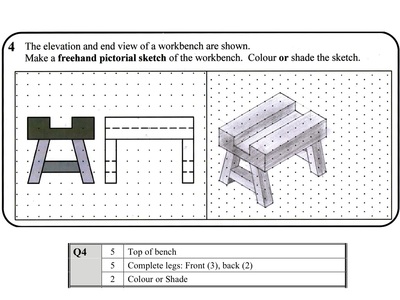
Isometric (Short Questions)
- Pictoral = 3D
- Horizontal lines become diagonal (at 30 degrees - use the dots)
- Vertical lines remain vertical
- Count the gaps between the dots to work out the length of the lines
- Don't forget to colour or shade the sketch
Click here for revision questions (note these will have to be printed)
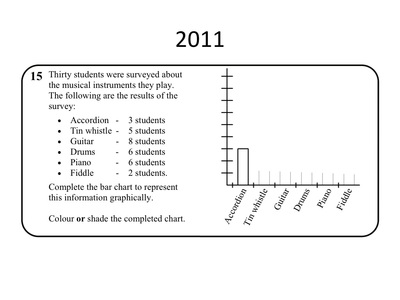
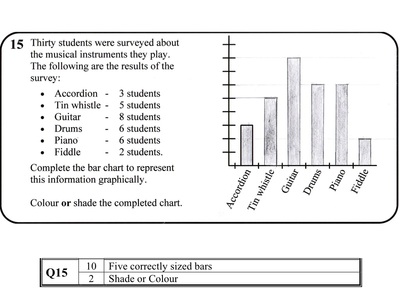
Graphs
Click here for revision questions (note: these will have to be printed)
Ellipse
- Know the circle method for drawing an ellipse
- Practice reading dimensions from a drawing
Sample Questions (draw on A3)
Solutions
Orthographic
- Know where to locate the different views (elevation, end view, plan) on the page
- Know how to project between the different views
Transformations
- Translation
- Axial symmetry
- Central symmetry
Sample Questions (Draw on A3)
Solutions
Isometric
- Know how to set up the isometric axes (30 degrees)
- Draw outline crates for key parts